Getting started with MongoDB databass

MongoDB is a multi-cloud document database service. In short it's a document-oriented database.
To easily get started with MongoDB, use MongoDB Atlas which is a fully managed cloud database on AWS, Azure, or GCP (Google Cloud Platform). In a web browser, navigate to https://www.mongodb.com/ and click on the Try Free button. Provide your email address, password and then follow the on-screen instructions to create a free account. You can also use your Google account to register.
Use coupon code MKT-VENKAT for $100 credit.

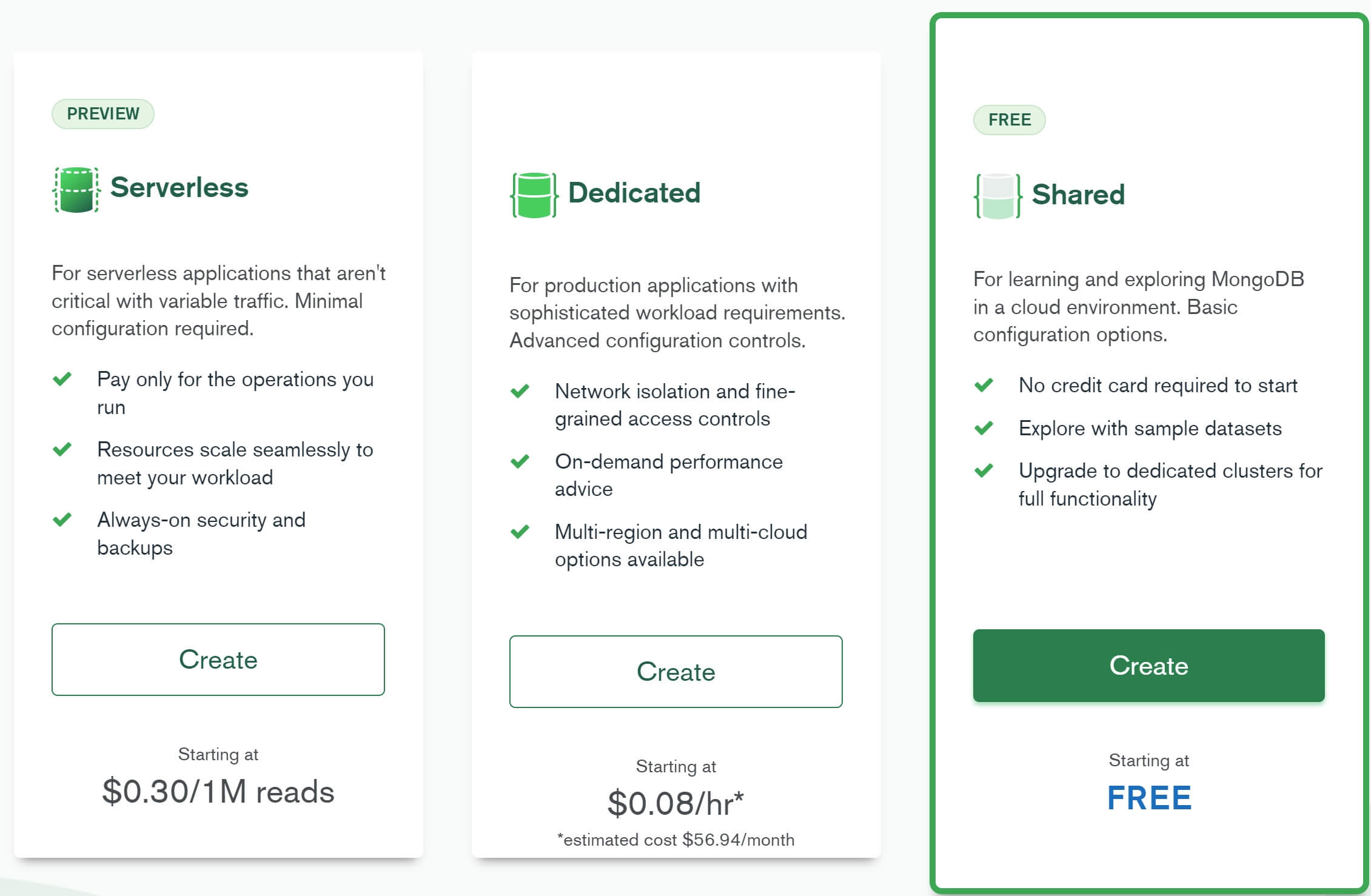
Use the free shared option to learn and explore MongoDB in a cloud environment. With the free option we get 512 MB of storage space, choose our preferred cloud provider - AWS, Google Cloud or Azure and the region where we want the Mongo database instance to be hosted.
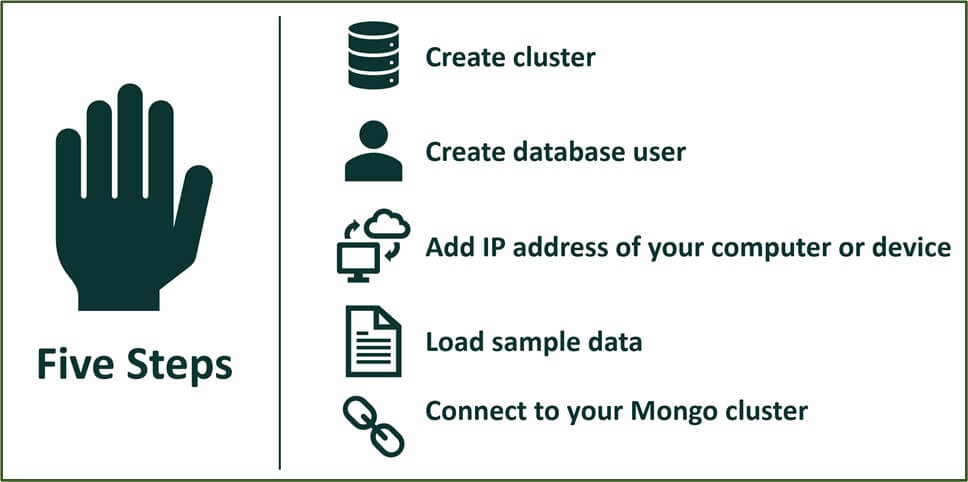
The following are the steps to get started with Mongo cluster in the cloud.
After the Mongo cluster is created, click on the Connect button.
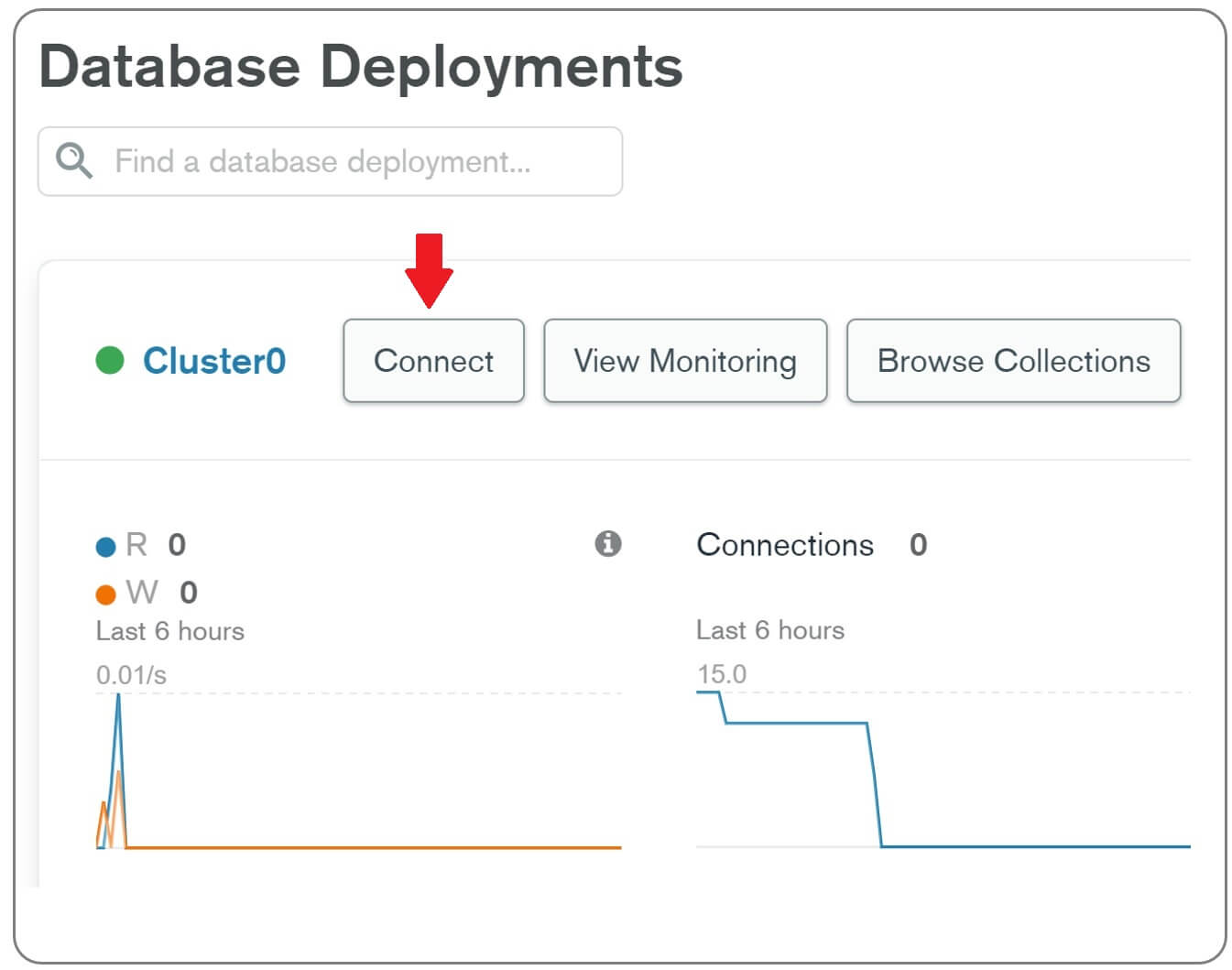
In the window that appears you have options to
- Create database users and
- Add IP addresses of machines that you want to allow to connect to your Mongo database
How to connect to MongoDB atlas
There are 3 ways we can connect to MongoDB Atlas.

- MongoDB Shell
- MongoDB Compass
- Custom Application
MongoDB Shell
MongoDB Shell is an interactive JavaScript interface for querying and modifying database data. We can also use it to perform administrative operations like creating databases, collections etc.
MongoDB Compass
MongoDB Compass is a GUI (Graphical User Interface) for querying, visualizing and modifying database data. Behind the scenes, both the Shell and Compass issues the same commands to the database server.
Your own custom application
You can also connect your own custom application. This application may be built using any technology (.NET, Java, PHP, Node, Python, etc), it doesn't matter.
Common Mongo Shell Commands
show dbs: Print a list of all databases on the server.use <dbname>: Switch current database to <dbname>.db: Displays the current database in use.show collections: Prints the list of collections in the current database.db.createCollection(): Creates a new collectiondb.collection.drop(): Drops or removes the collection completely.db.collection.insertOne(): Insert a new document into the collection.db.collection.insertMany(): Insert multiple new documents into the collection.db.collection.updateOne(): Update a single existing document in the collection.db.collection.updateMany(): Update multiple existing documents in the collection.db.collection.deleteOne(): Delete a single document from the collection.db.collection.deleteMany(): Delete documents from the collection.db.collection.createIndex(): Create a new index on the collection if the index does not exist; otherwise, the operation has no effect.
db.collection.insertOne() example
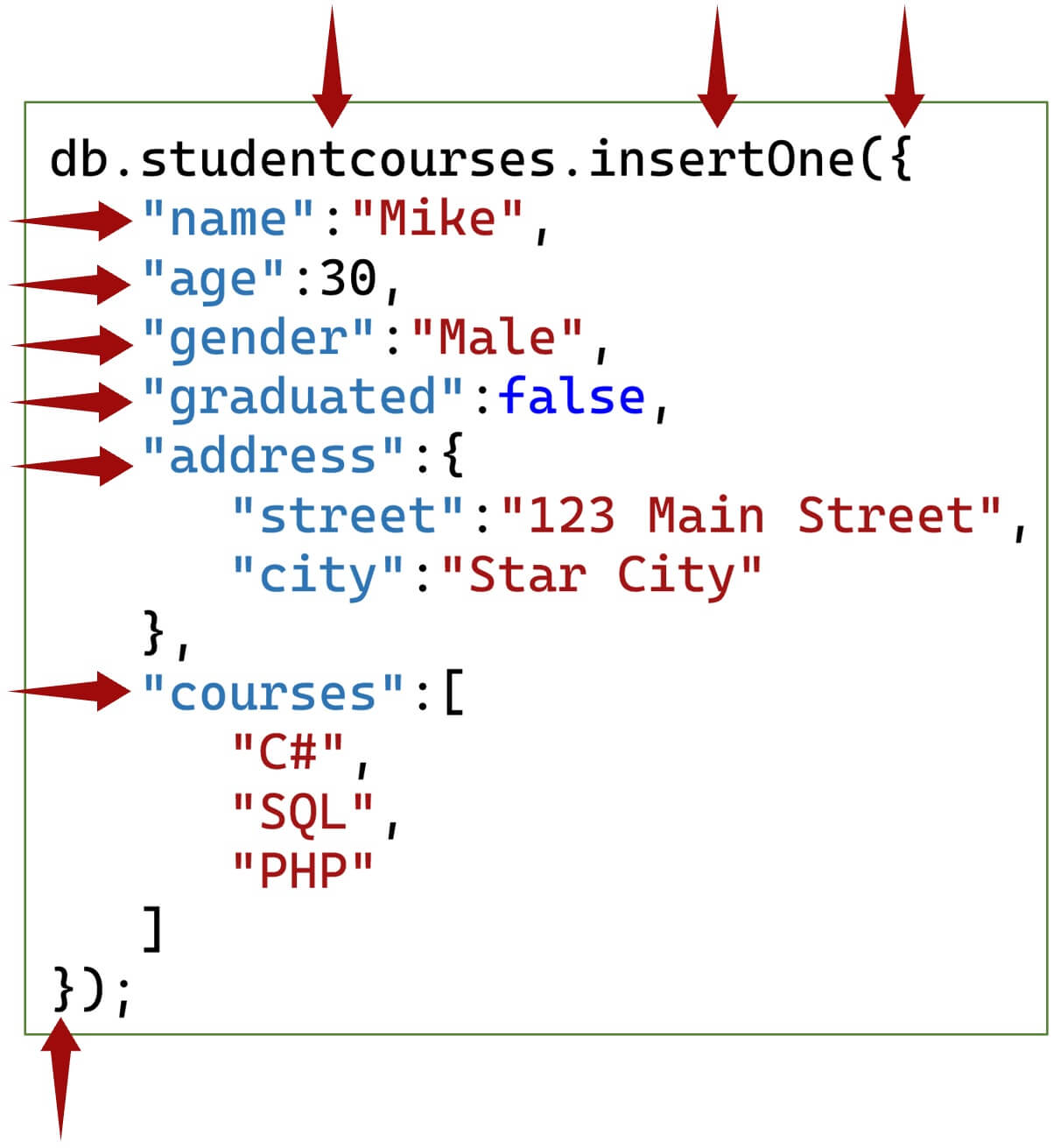
db.collection.insertMany() example
db.studentcourses.insertMany([
{
"name": "Mary",
"age": 28,
"gender": "Female",
"graduated": true,
"address": {
"street": "99 George Street",
"city": "Super City"
},
"courses": [ "ASP.NET", "LINQ", "Angular" ]
},
{
"name": "Pam",
"age": 29,
"gender": "Female",
"graduated": false,
"address": {
"street": "101 King Street",
"city": "Mongo City"
},
"courses": [ ".NET Core", "C++", "Bootstrap" ]
},
{
"name": "Ben",
"age": 31,
"gender": "Male",
"graduated": true,
"address": {
"street": "35 Queen Street",
"city": "London"
},
"courses": [ "JavaScript", "C#", "HTML" ]
}
]);MongoDB collection find examples
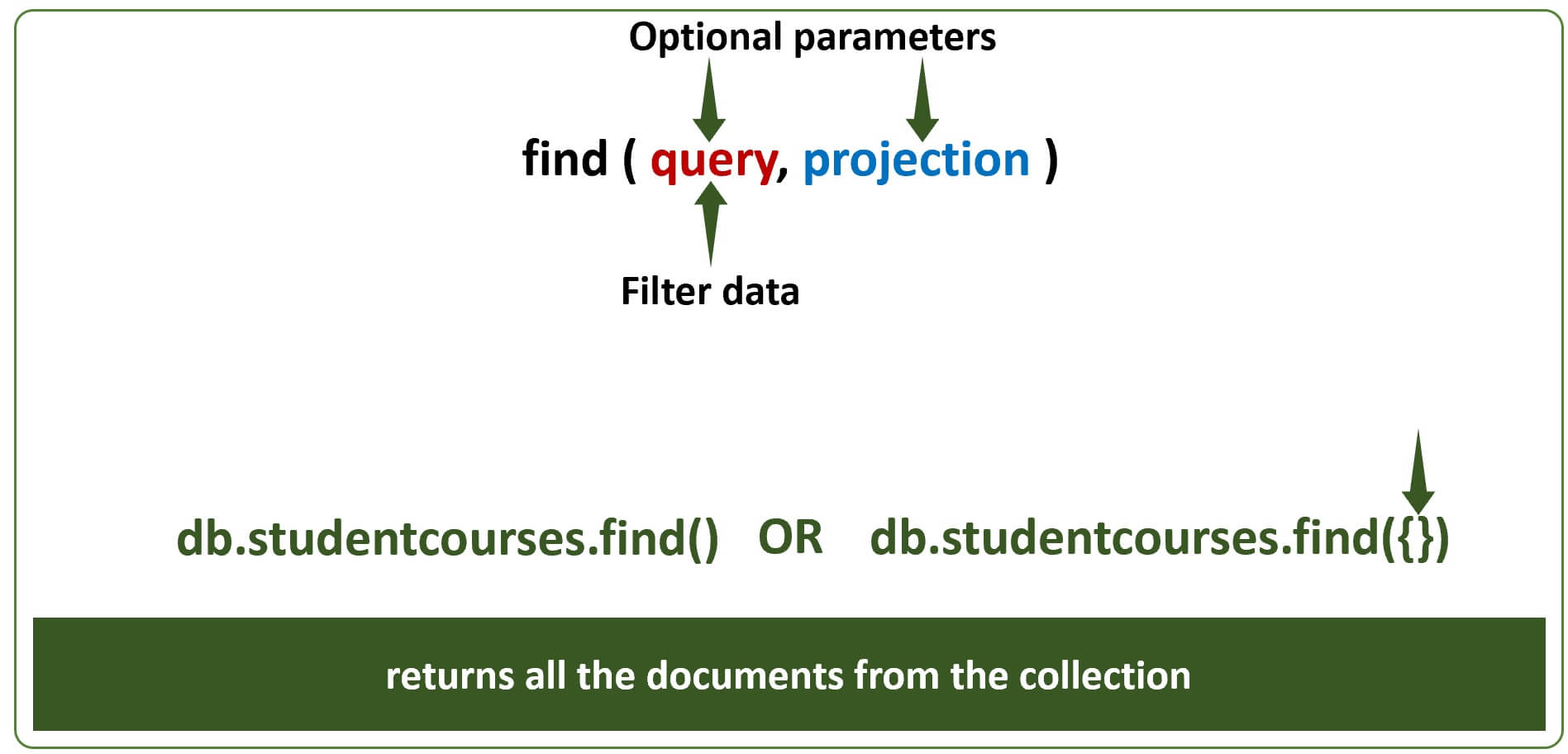
- Use
find()method to find documents in a collection. - find() method has two parameters -
query&projecttion. - Both are optional parameters.
- Use the
queryparameter to filter data. - You can think of it as a
WHEREclause in SQL. find()method returns all the documents in a collection, if we do not include the query parameter or pass an empty object ({}).
Find all documents in studentcourses collection where name is Ben
db.studentcourses.find({name: "Ben"})Find all documents in studentcourses collection where age is 28
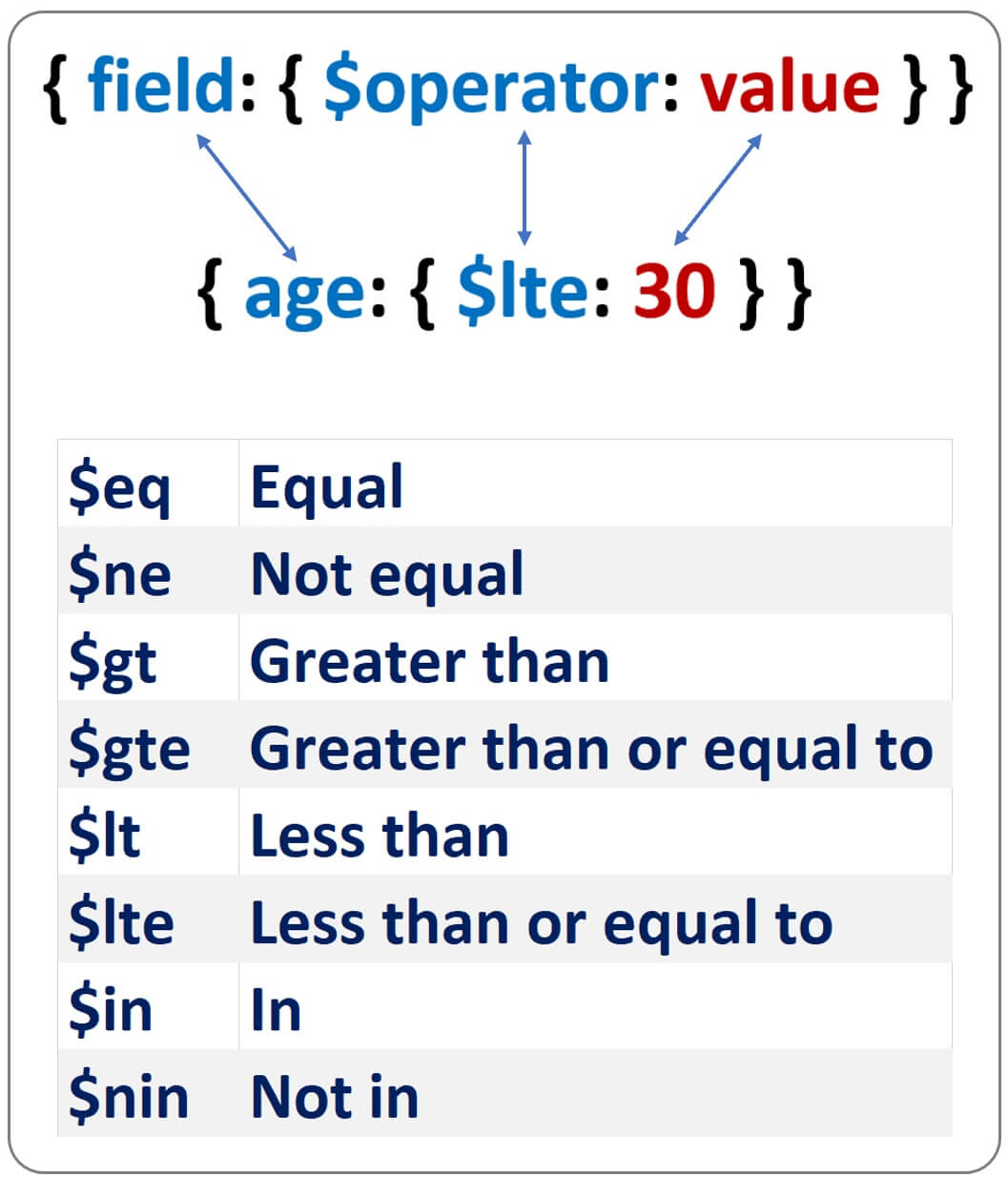
db.studentcourses.find({age: 28})Find all documents where age is less then or equal to 30
db.studentcourses.find({age: {$lte: 30}})MongoDB query operators examples
Find all documents where age in [ 28, 29, 30 ]
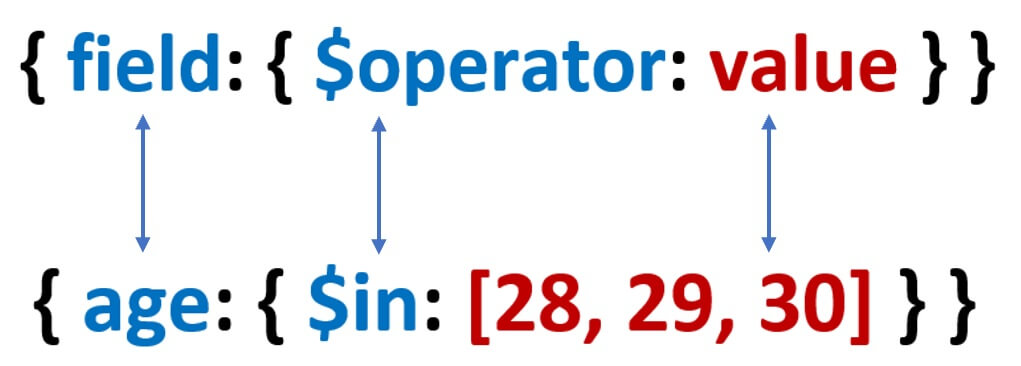
db.studentcourses.find({age: {$in: [28, 29, 30]}})MongoDB find projection example

- By default, queries in MongoDB return all fields in matching documents.
- To limit the amount of data that MongoDB returns, you can include a projection.
- A projection basically tells what fields to include or exclude in the matching documents.
- Use 1 to include a field and 0 to exclude a field.
Include only name and age fields in the result
db.studentcourses.find({age: {$lte: 30}}, {name:1, age:1})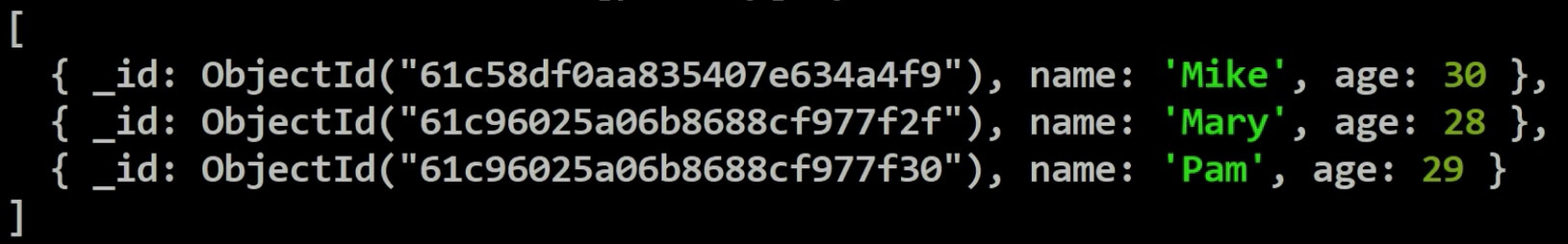
_id field is always returned. To exclude it, you have to explicitly specify it using an exclusion projection (_id:0) as shown below.
db.studentcourses.find({age: {$lte: 30}}, {name:1, age:1, _id:0})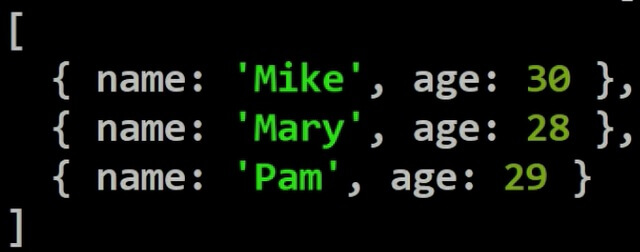
Inclusion and exclusion projection
- You cannot specify the fields that you want to include and exclude at the same time in a projection.
- You can only specify an inclusion projection or exclusion projection.
- _id field is the only exception.
The following projection results in error - Cannot do exclusion on field age in inclusion projection
{name: 1, age: 0}MongoDB find in nested object

addressis a nested JSON document.- Find all documents where
cityisStar City.
db.studentcourses.find({"address.city": "Star City"})MongoDB find cursor example
![]()
findmethod returns a cursor.- You can think of the cursor as a virtual object that stores the documents returned by the find method.
- So this means along with the find method we can also use methods like
count,sort,skip,limitetc. - These 3 methods - sort, skip and limit are particularly useful to implement server side sorting and paging.
Find the total count of documents in a collection
db.studentcourses.find().count()Find the total count of documents where gender is Female
db.studentcourses.find({gender: "Female"}).count()Mongodb sort example
- To sort documents in MongoDB use sort() method.
- 1 to sort in ascending order and -1 in descending order.
Sort documents by age field in descending order
db.studentcourses.find().sort({"age":-1})Sort documents by age field in descending order and then by name in ascending order.
db.studentcourses.find().sort({"age":-1, "name": 1})Sort by age field in descending order, skip first 1 document and take only the next 2 documents
db.studentcourses.find().sort({"age":-1}).skip(1).limit(2)MongoDB updateOne example
Update name to Sara and age to 100 where name is Mary.
db.studentcourses.updateOne({"name":"Mary"},{$set: {"name":"Sara", "age":100}})MongoDB updateMany example
Update gender in all documents to Unknown where gender is Female
db.studentcourses.updateMany({"gender":"Female"},{$set: {"gender":"Unknown"}})MongoDB deleteOne example
Delete one document where name is Sara
db.studentcourses.deleteOne({"name":"Sara"})MongoDB deleteMany example
Delete all document where age is less than 31
db.studentcourses.deleteMany({"age":{$lt:31}})MongoDB Compass Commands
Find all documents in a collection
{}Find all documents where name = "Venkat"
{name: "Venkat"}The above query can also be written as shown below. In this example we are using the equal ($eq) query operator.
{name: {$eq: "Venkat"}}Filter, project and sort example - All in one query
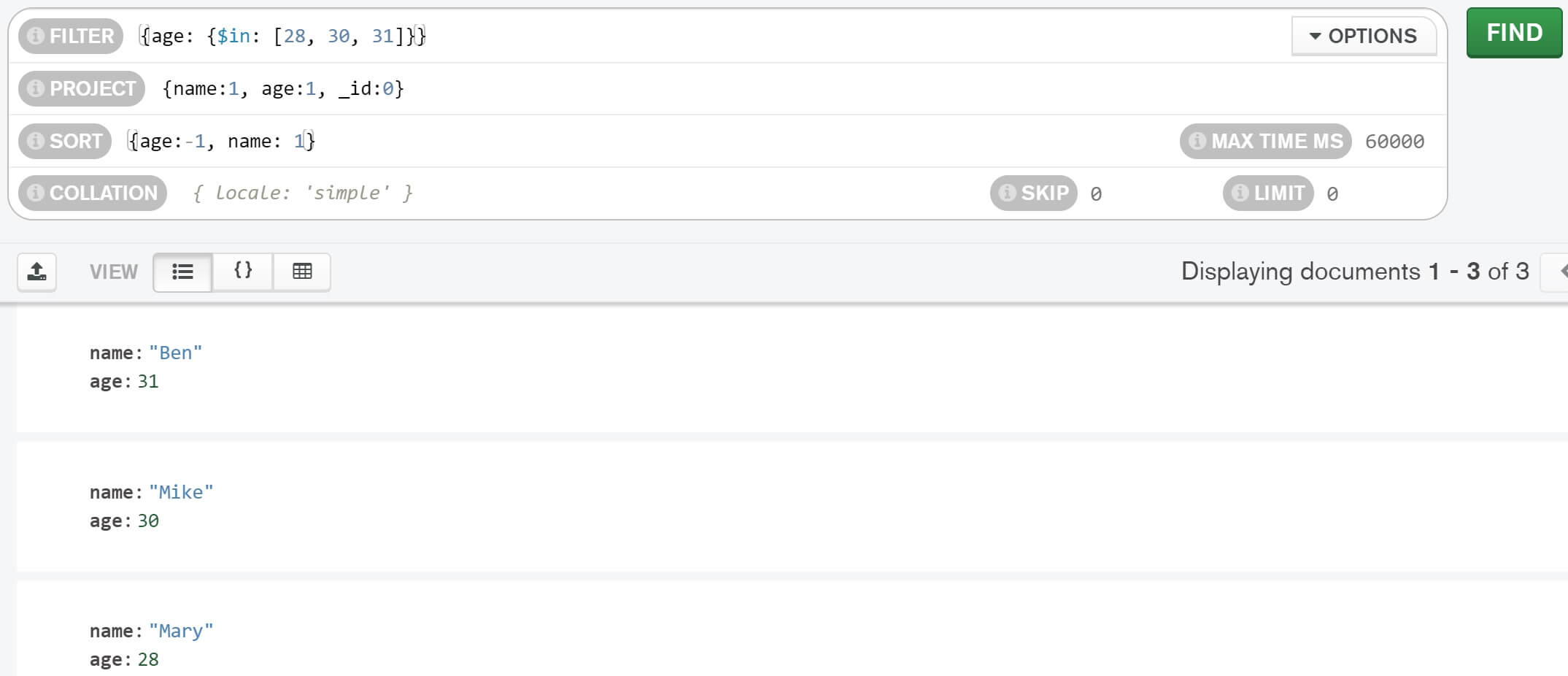
Summary
- MongoDB Atlas - Mongo Database in the cloud (Azure, AWS or GCP).
- MongoDB Shell - CLI (Command Line Interface) interface to write and test Mongo database queries.
- MongoDB Compass - Graphical User Interface to connect to and work with Mongo databases. It is the easiest way to interact with your data in MongoDB. Under the hood, Compass uses Mongo Shell.
© 2020 Pragimtech. All Rights Reserved.

